CATALOGUE >
Release 8.7
ω
ω
APPENDIX >
Technical information about products
a
APPENDIX
Calculation:
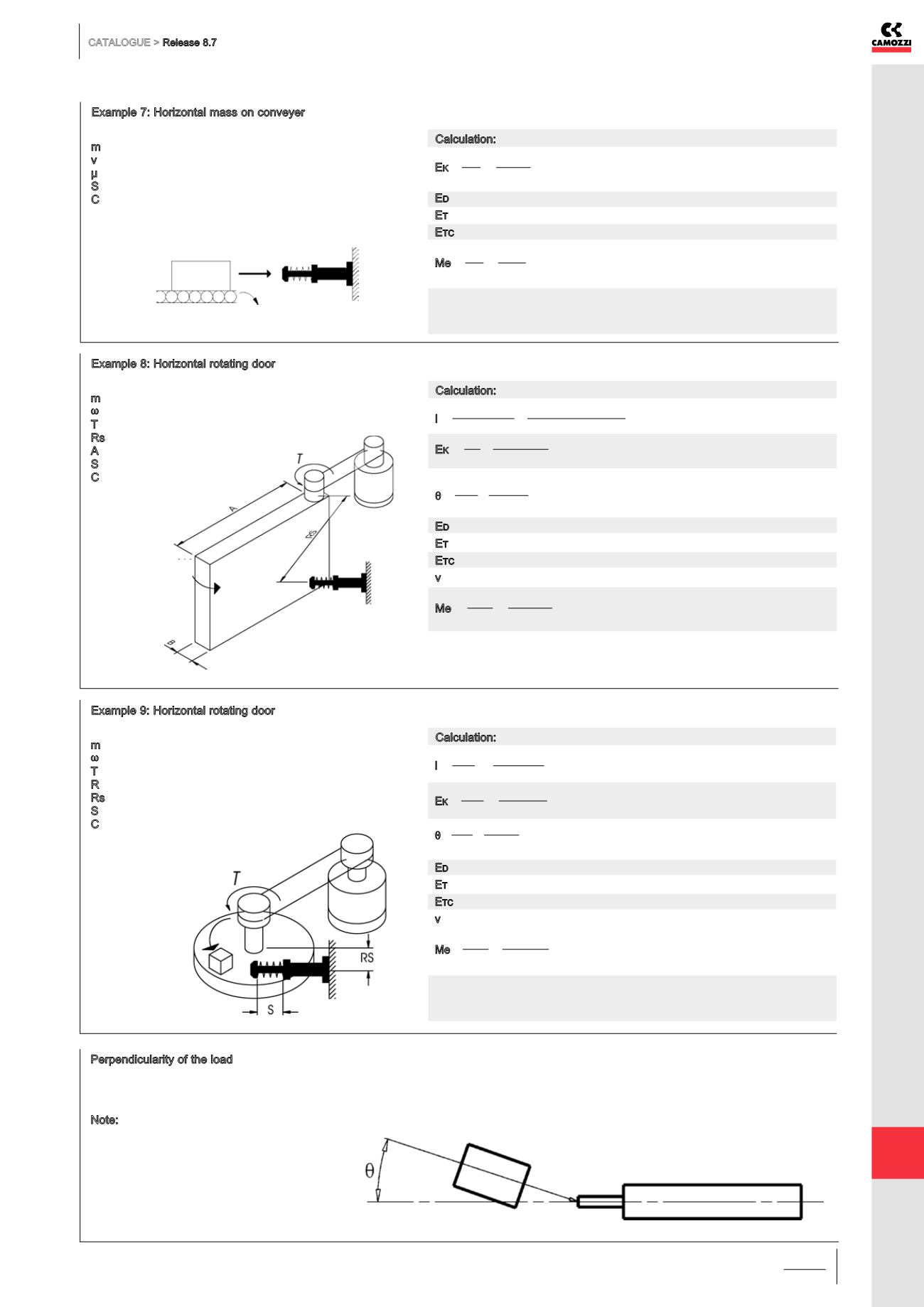
Example 7: Horizontal mass on conveyer
The adequate shock absorber to use in this case is Mod. SA 0806
according to the technical data, where we find that E
t
(max) = 3 Nm,
E
tc
(max) = 7000 Nm/h and Me (max) = 6 kg.
Application data:
m = 5 kg
v = 0,5 m/s
µ = 0,25
S = 0.006 m
C = 3000 cycles/h
E
k
= mv
2
= 5 . 0,5
2
= 0,63 Nm
2 2
E
d
= F . S = m . g . µ . s = 5 . 9,81 . 0,25 . 0,006 = 0,07 Nm
E
t
= E
k
+ E
d
= 0,63 + 0,07 = 0,7 Nm
E
tc
= E
t
. C = 0,7 . 3000 = 2100 Nm/h
Me = 2E
t
= 2 . 07 = 5,6 Kg
v
2
0,5
2
Example 8: Horizontal rotating door
Application data:
m = 20 kg
ω
= 2,0 rad/s
T = 20 Nm
Rs = 0,8 m
A = 1,0 m
S = 0,015 m
C = 600 cycles/h
Calculation:
l = m (4A
2
+ B
2
) = 20(4 . 1,0
2
+ 0,05
2
) = 6,67 Kg . m
2
12 12
E
k
= l
ω
2
= 6,67 . 2,0
2
= 13,34 Nm
2 2
θ
= S = 0,015 = 0,019 rad
Rs 0,8
E
d
= T .
θ
= 20 . 0,018 = 0,36 Nm
E
t
= E
k
+ E
d
= 13,34 + 0,36 = 13,7 Nm
E
tc
= E
t
. C = 13,7 . 600 = 8220 Nm/h
v =
ω
. Rs = 2,0 . 0,8 = 1,6 m/s
Me = 2 E
t
= 2 . 13,7 = 10,7 Kg
v
2
1,6
2
The adequate shock absorber to use in this case is Mod. SA 1412
according to the technical data, where we find that E
t
(max) = 20 Nm,
E
tc
(max) = 33000 Nm/h and Me (max) = 40 kg.
Calculation:
Example 9: Horizontal rotating door
Application data:
m = 200 kg
ω
= 1,0 rad/s
T = 100 Nm
R = 0,5 m
Rs = 0,4 m
S = 0,015 m
C = 100 cycles/h
The adequate shock absorber to use in this case is Mod. SA 2015
according to the technical data, where we find that E
t
(max) = 59 Nm,
E
tc
(max) = 38000 Nm/h and Me (max) = 720 kg.
To ensure the lifetime of the shock absorber, the movement of the impact body
must be perpendicular to the shock absorbers axial centre.
Note: The maximum allowable eccentricity
θ
≤ 2,5° (0,044 rad).
Perpendicularity of the load
Load
l = mR
2
= 200 . 0,5
2
= 25 Kg . m
2
2 2
E
k
= l
ω
2
= 25 . 1,0
2
= 12,5 Nm
2 2
θ
= S = 0,015 = 0,0375 rad
Rs 0,4
E
d
= T .
θ
= 100 . 0,0375 = 3,75 Nm
E
t
= E
k
+ E
d
= 12,5 + 3,75 = 16,25 Nm
E
tc
= E
t
. C = 16,25 . 100 = 1625 Nm/h
v =
ω
. Rs = 1,0 . 0,4 = 0,4 m/s
Me = 2 E
t
= 2 . 16,25 = 203 Kg
v
2
0,4
2
a
/3.05
03