Products designed for industrial applications.
General terms and conditions for sale are available on
www.camozzi.com.1
Series ARP actuators
MOVEMENT >
CATALOGUE
>
Release 8.8
/6.20.03
1
MOVEMENT
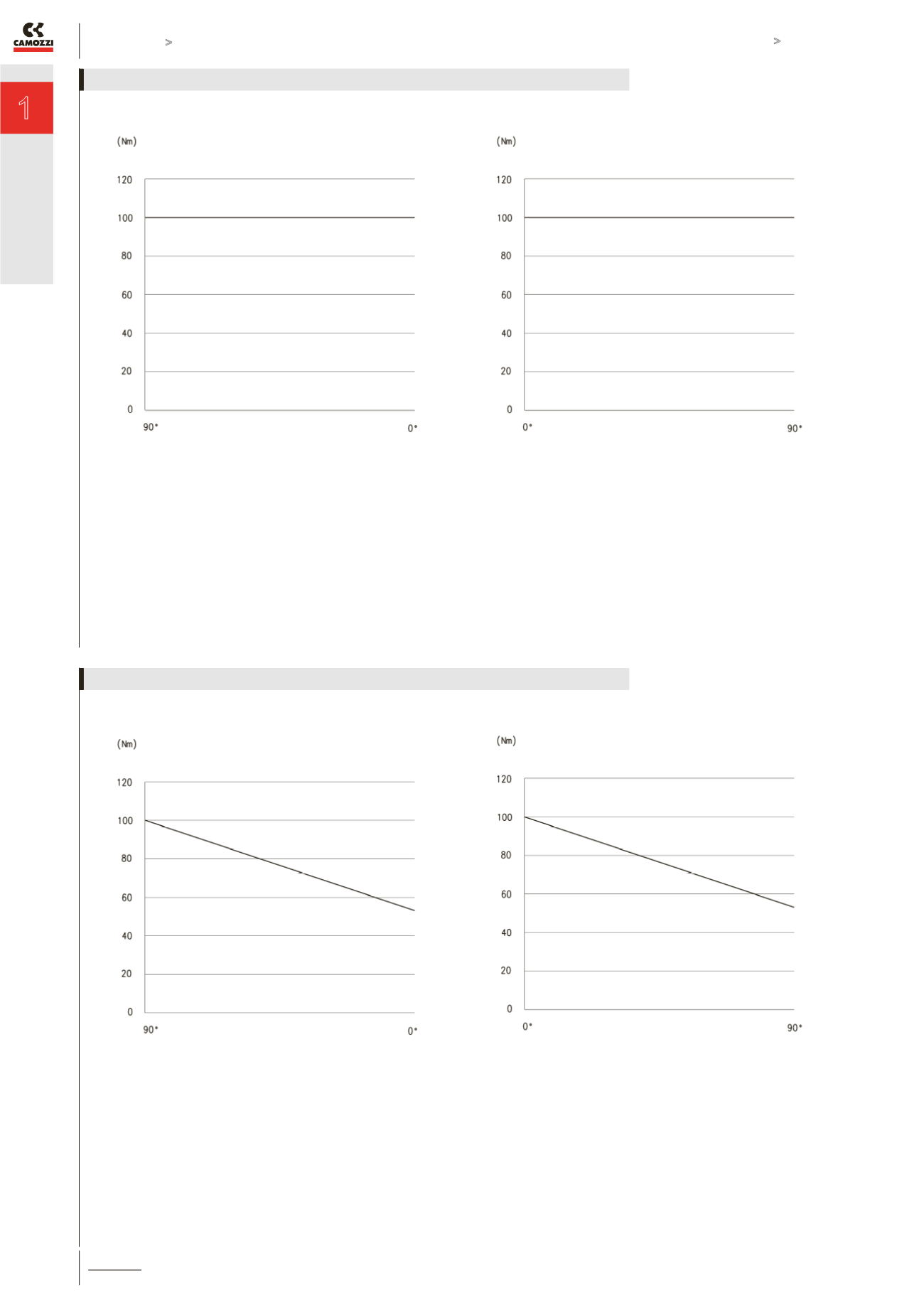
The above graph shows the torque force (in Nm) generated by
a double-acting rotary actuator Series ARP during the closing
action. The action starts from the 90° position and finishes at 0°.
One of the features/advantages with a “rack and pinion” style
rotary actuator is that the generated torque force is constant
throughout the whole movement.
See also the TORQUE FORCE TABLE on page 1/6.20.04.
The above graph shows the torque force (in Nm) generated by
a double-acting rotary actuator Series ARP during the opening
action. The action starts from the 0° position and finishes at 90°.
One of the features/advantages with a “rack and pinion” style
rotary actuator is that the generated torque force is constant
throughout the whole movement.
See also the TORQUE FORCE TABLE on page 1/6.20.04.
TORQUE FORCE DIAGRAM GENERATED BY A DOUBLE-ACTING ACTUATOR
The above graph shows the torque force (in Nm) generated by
a single-acting rotary actuator Series ARP during the closing
action. The action starts from the 90° position and finishes at
0°. The generated torque force is at the highest at 90°, while it
decreases along the stroke due to the fact that the springs get
less compressed. In this case it is the springs which generates
the driving force.
See also the TORQUE FORCE TABLE on page 1/6.20.04.
The above graph shows the torque force (in Nm) generated by
a single acting rotary actuator Series ARP during the opening
action. The action starts from the 0° position and finishes at
90°. The generated torque force is at the highest at 0°, while it
decreases along the stroke due to the fact that the springs get
more compressed, (the counter force increases). In this case it is
the compressed air which generates the driving force.
See also the TORQUE FORCE TABLE on page 1/6.20.04.
TORQUE FORCE DIAGRAM GENERATED BY A SINGLE-ACTING ACTUATOR