CATALOGUE >
Release 8.8
APPENDIX >
Technical information about products
a
APPENDIX
Calculation:
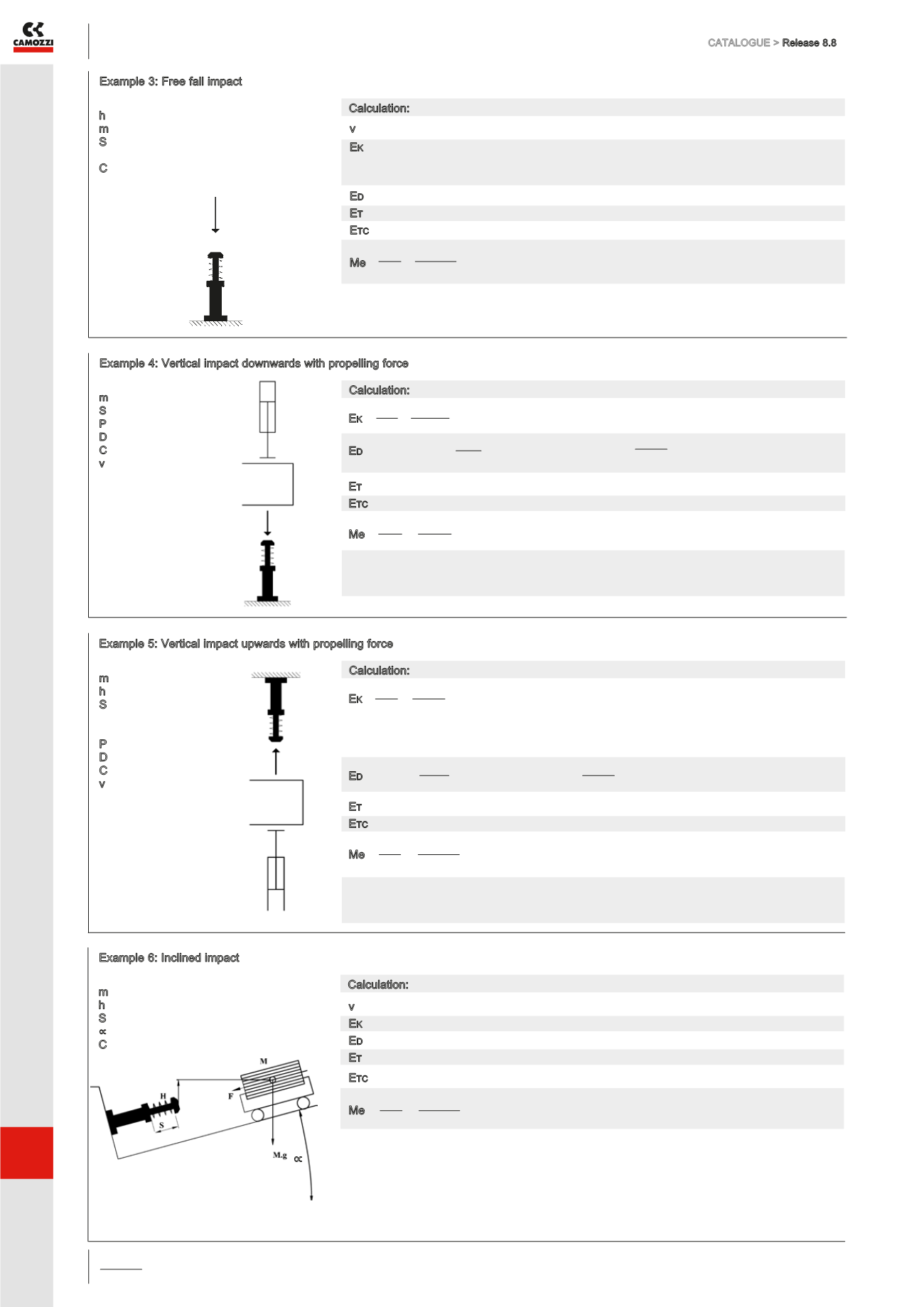
Example 3: Free fall impact
Application data:
h = 0,35 m
m = 5 kg
S = 0.01 m
first hypothesis SA 1210
C = 1500 cycles/h
v = √ (2g . h) √ (2 . 9,81 . 0,35) = 2,6 m/s
E
k
= m . g . h = 5 . 9,81 . 0,35 = 17,2 Nm
Consider the shock absorber with the lowest E
t
but superior to 17.2 Nm:
mod. SA 1412 S = 0.012 m
E
d
= F . S = m . g . s = 5 . 9,81 . 0,012 = 0,6 Nm
E
t
= E
k
+ E
d
= 17,2 + 0,6 = 17,8 Nm
E
tc
= E
t
. C = 17,8 . 1500 = 26700 Nm/h
Me = 2E
t
= 2 . 17,5 = 5 Kg
v
2
2,6
2
Calculation:
Example 4: Vertical impact downwards with propelling force
The adequate shock absorber to use in this case is Mod. SA 2725 according
to the technical data, where we find that E
t
(max) = 147 Nm,
E
tc
(max) = 72000 Nm/h and Me (max) = 270 kg.
The adequate shock absorber to use in this case is Mod. SA 1412 according
to the technical data, where we find that E
t
(max) = 20 Nm,
E
tc
(max) = 33000 Nm/h and Me (max) = 40 kg.
Application data:
m = 50 kg
S = 0.025 m
P = 6 bar
D = 63 mm
C = 600
cycles
/h
v = 1,0 m/s
Calculation:
Example 5: Vertical impact upwards with propelling force
Application data:
m = 50 kg
h = 0.3 m
S = 0.025 m
first hypothesis
Mod. SA 2525
P = 6 bar =0,6 MPa
D = 63 mm
C = 600 cycles/h
v = 1,0 m/s
E
k
= mv
2
= 50 . 1
2
= 25 Nm
2 2
Consider the shock absorber with the lowest E
t
but superior to 25 Nm:
mod. SA 2015 S=0.015 m
E
d
= F . S = ( D
2
.
π
. P . g/100 – m . g) . S = ( 63
2
.
π
6 . 9,81/100 – 50 . 9,81) . 0,015 = 20,1 Nm
4
4
E
t
= E
k
+ E
d
= 25 + 20,1 = 45,7 Nm
E
tc
= E
t
. C = 45,1 . 600 = 27060 Nm/h
Me = 2
E
t
= 2 . 45,7 = 91,4 Kg
v
2
1
2
E
k
= mv
2
= 50 . 1
2
= 25 Nm
2 2
E
d
= F . S = (m . g + D
2
.
π
. P . g/100 ) . S = (50 . 9,81 + 63 .
π
. 6 . 9,81/100) . 0,025 = 58,1 Nm
4
4
E
t
= E
k
+ E
d
= 25 + 58,1 = 83,1 Nm
E
tc
= E
t
. C = 83,1 . 600 = 49860 Nm/h
Me = 2
E
t
= 2 . 84 = 168 Kg
v
2
1
2
The adequate shock absorber to use in this case is Mod. SA 2015 according
to the technical data, where we find that E
t
(max) = 59 Nm,
E
tc
(max ) = 38000 Nm/h and Me (max )= 120 kg.
Calculation:
Example 6: Inclined impact
Application data:
m = 10 kg
h = 0,3 m
S = 0.015 m
∝
= 30°
C = 600 cycles/h
v = √ (2g . h) √ (2 . 9,81 . 0,3) = 2,43 m/s
E
k
= m . g . h 10 . 9,81 . 0,3 = 29,4 Nm
E
d
= F . S = m . g . sin
α
. s = 10 . 9,81 . sin30° . 0,015 = 10 . 9,81 . 0,5 . 0,015 = 0,7 Nm
E
t
= E
k
+ E
d
= 29,4 + 0,7 = 30,1 Nm
E
tc
= E
t
. C = 30,1 . 600 = 18060 Nm/h
Me = 2
E
t
= 2 . 30,1 = 10,2 Kg
v
2
2,43
2a
The adequate shock absorber to use in this case is Mod. SA 2015 according
to the technical data, where we find that E
t
(max) = 59 Nm,
E
tc
(max) = 38000 Nm/h and Me (max) = 120 kg.
∝
a
/3.05