
VALVES
A
B
3
2
1
3/2-way NC solenoid valve
(3-way, 2-position, normally closed)
Figure 23
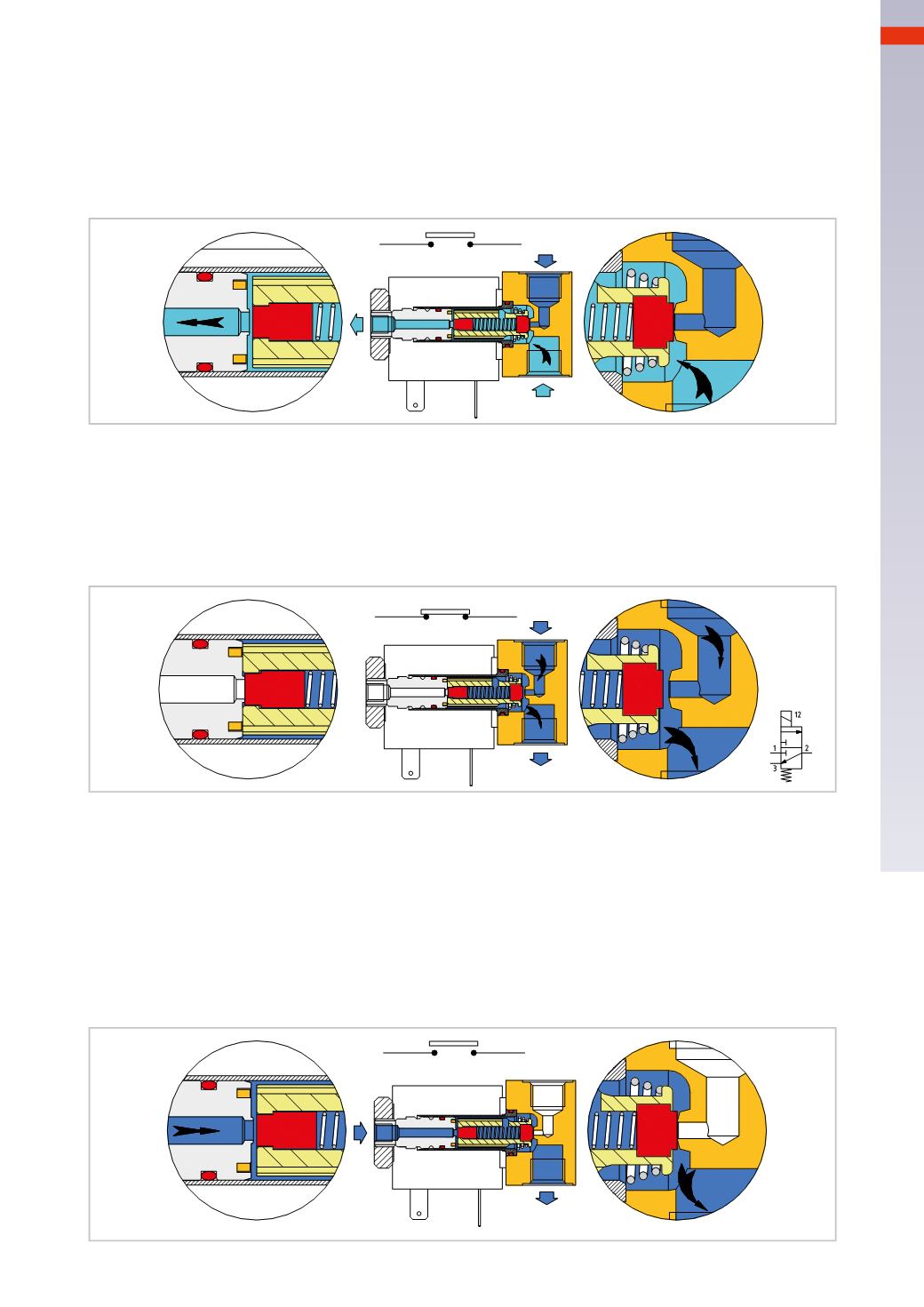
Rest position, electrical contact open, absence of electrical energy.
Pos. A
: the conical spring pushes the mobile plunger and its seal against the orifice, closing the passage of C/A
from inlet 1 towards outlet 2.
Pos. B
: under the action of the conical spring, the upper part of themobile plunger and its seal, are detached from
the fixed plunger, putting outlet 2 in communicationwith the exhaust 3.
Fig. 23
Figure 24
The electrical contact is closed, there is passage of electrical energy, voltage is supplied to the solenoid.
Pos. C
: a current flows through the solenoid generating amagnetic field that attracts themobile plunger upwards.
The conical spring compresses and the seal is detached from the orifice. It opens the passage of C/A from inlet 1 to
outlet 2.
Pos. D
: the surface of the upper part of themobile plunger is in contact with the lower surface of the fixed plunger,
the seal closes the passage towards the exhaust 3.
C
D
3
2
1
Fig. 24
3/2-way NO solenoid valve
(3-way, 2-position, Normally Open)
In comparisonwith the 3/2-way NC solenoid valvewe observe the following differences:
• the location of inlet 1 and exhaust 3;
• the load of the internal springs.
Figure 25
Rest position, electrical contact open, absence of electrical energy.
Pos. A
: the conical spring pushes themobile plunger and its seal against the orifice closing the passage of C/A from
inlet 1 to exhaust 3.
Pos. B
: under the influence of the conical spring, theupper section of themobile plunger and its seal, are detached
from the fixed plunger, putting inlet 1 in communicationwith outlet 2.
A
B
3
2
1
Fig. 25
4
103
CAMOZZI
>
VALVES

















