
VALVES
Fig. 37
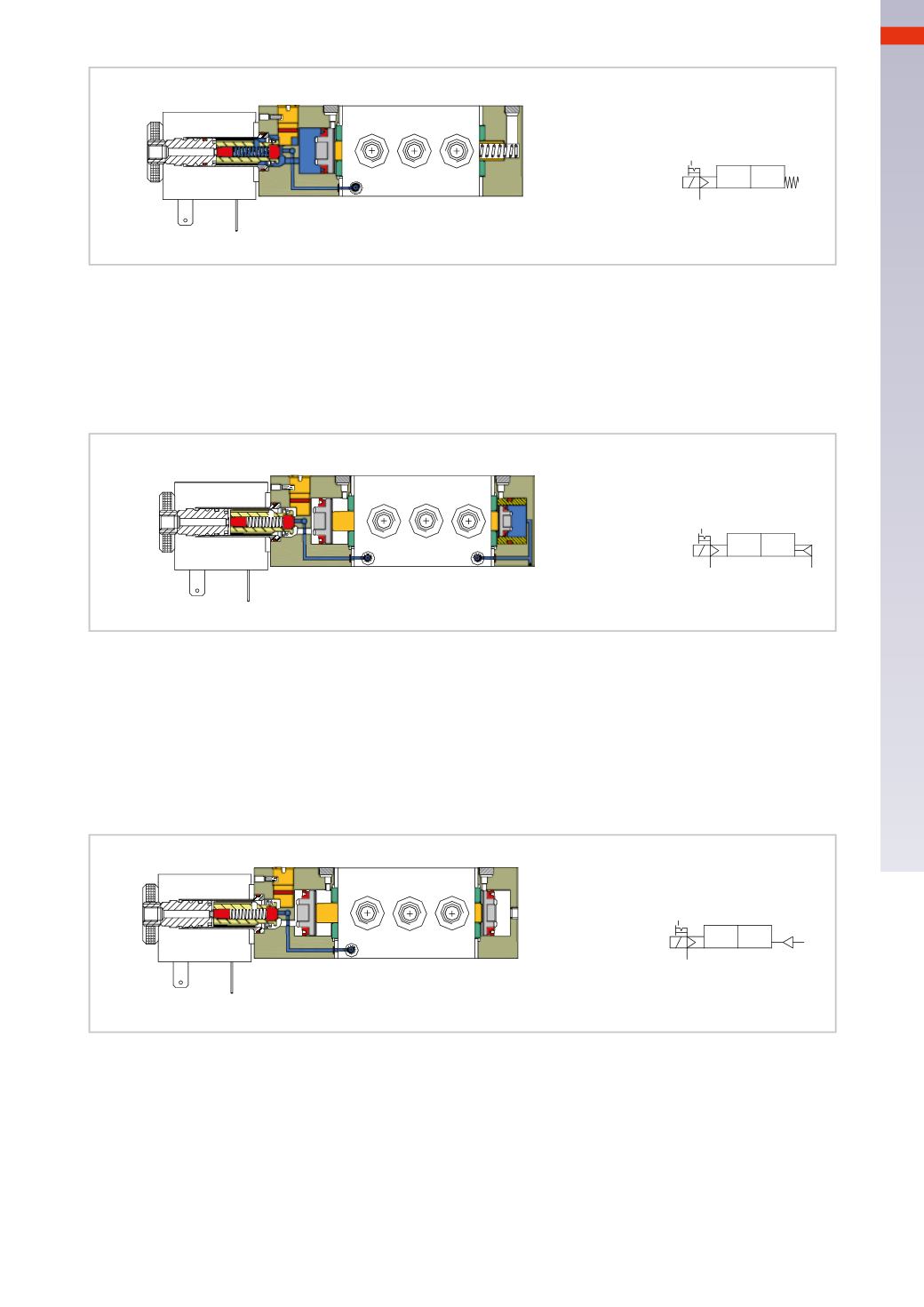
Figure 38
Solenoid valvewith electric command, pneumatic spring return and external pilot air
In contrast to the previous situation, there is a pneumatic spring instead of a mechanical spring. The pneumatic
spring is comprised of a small piston, powered by an external source, but with smaller dimensions than the piston
on the end cap with the solenoid. In the situation where the solenoid is not energized, and there is compressed
air, the solenoid valve assumes the position determined by the pneumatic spring. This solenoid valve is called
Monostablewith external pneumatic spring return and external servo pilot.
Fig. 38
Figure 39
Solenoid valvewith electric command, pneumatic return and external servo pilot
The end cover on the right, commonly called “pneumatic end cover”, has a threaded port to which an external
pilot can be connected. The two pilot pistons have the same diameter. The repositioning of the spool occurs only
in the presence of external pneumatic piloting. As the electrical signal ceases, the valve position does not change,
it does soonly in thepresence of an external pilot signal. This solenoid valve is calledBistablewith electric command,
pneumatic return and external servo pilot. If the pneumatic return signal were to be always present but with
reduced pressure, the valvewouldbeMonostablewith an electric command, pneumatic spring return and external
servo pilot.
Fig. 39
4
109
CAMOZZI
>
VALVES

















