
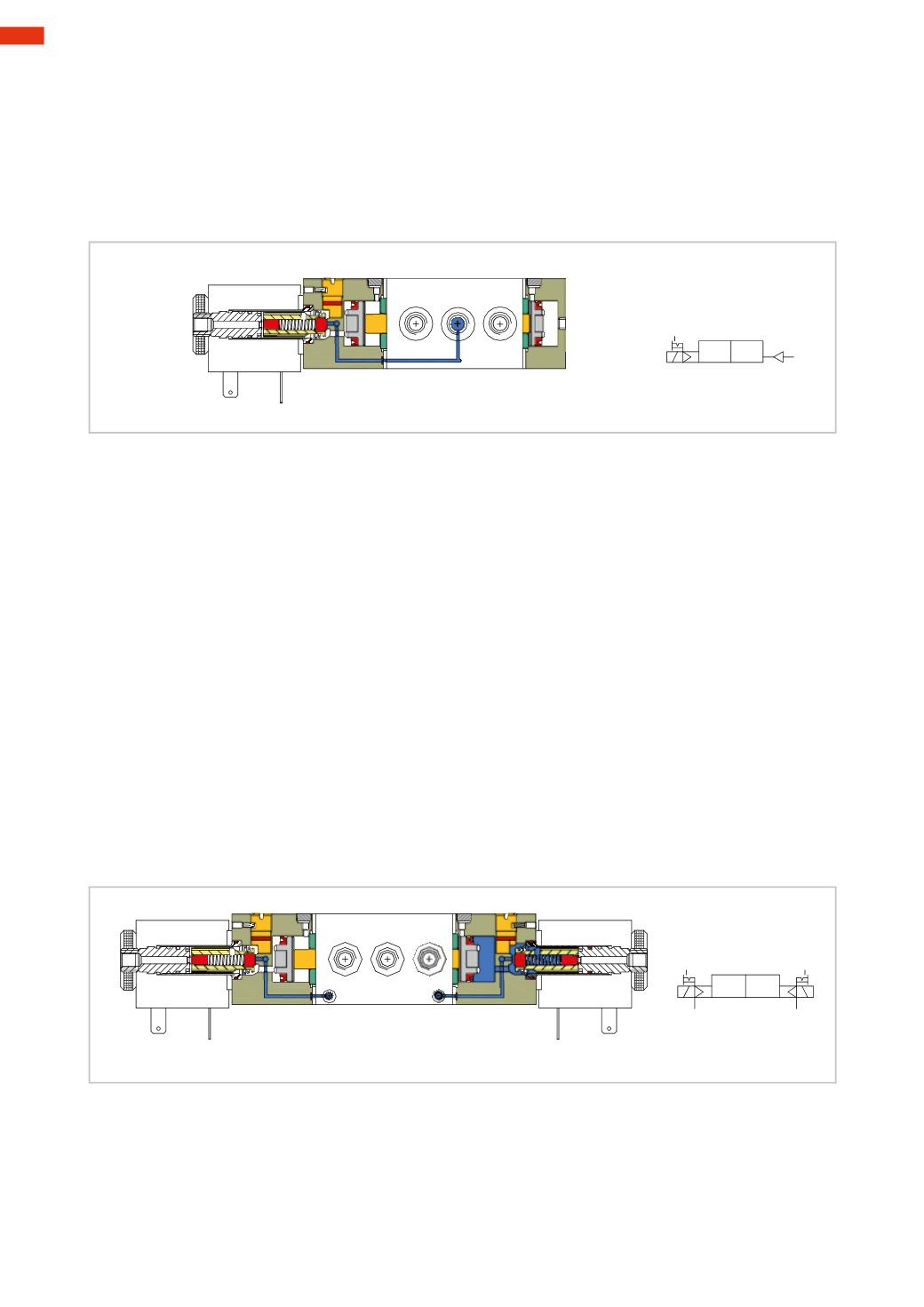
Figure 35
Solenoid valvewith electric command and pneumatic return
The end cap to the right, commonly called “pneumatic end cap”, has a threaded port to which an external pilot
can be connected. The two control pistons have the same diameter. The repositioning of the spool takes place only
in the presence of external pneumatic piloting. When removing the electrical signal from the solenoid, the valve
position does not change, it does so only in the presence of an external pilot. In this condition it is called aBistable
with electric commandwith external pneumatic repositioning.
In the situationwhere the external pneumatic command is always present thoughwith reduced pressure, the valve
would beMonostablewith electric commandwith pneumatic repositioning spring.
Fig. 35
Solenoid valves with external servo pilot
As shown in indirect command valves this is a solenoid valve, which provides control to the pilot (signal) by
opening or closing a passage of compressed air.
The pneumatic supply to the solenoid is the same as that supplied to themain solenoid valve and is obtained via
an internal channel to the valve. Depending on the type of solenoid valve the minimum pressure required for
piloting control is approx. 2 bar. In situationswhere a low pressure or vacuum is used, it is necessary to supply the
solenoid valvewith a different pilot pressure. In this situation, the solenoid valves that have a separate connection
for the power supply are used and are defined as
with external servo pilot
.
There are no particular differences between the two types.
Figure 36
Solenoid valvewith dual electric command and external servo pilot
The central body is that of a normal valve where the channeling of the servo-pilot is absent or intercepted. Each
end of the body is closed by an end cover which has the function of a pilot valve. The air supply of themain valve
is independent from that of the pilot valve, the output of air drives their respective pilot pistons. The solenoid on the
right is energized; the outgoing pilot airmoves the pilot piston, whichmoves the spool to the left. In this phase, the
solenoid valve on the left should not be energized. When removing the electrical signal to the solenoid, the valve
holds the position. This solenoid valve is calledBistablewith external servo pilot.
Fig. 36
Figure 37
Solenoid valvewith electric command, mechanical spring return and external servo pilot
In this case, the solenoid on the right has been replaced by a mechanical spring. The solenoid on the left is
energized, the outgoing airmoves the pilot piston,whichmoves the spool to the right, the return spring compresses.
When releasing the electrical signal to the solenoid, the solenoid valve returns to its rest position due to the effect
of the spring. When the solenoid is not energized, the solenoid valve assumes the position defined by the spring.
This solenoid valve is calledMonostablewithmechanical spring return and external servo pilot.
4
108
CAMOZZI
>
VALVES

















