
Usage of valves with vacuum
Not all of the valves can be usedwith a vacuum, several parametersmust be taken into consideration such as: the
internal construction, the type of switching, the type of seals used and other factors.
We examinemini poppet valves as an example:
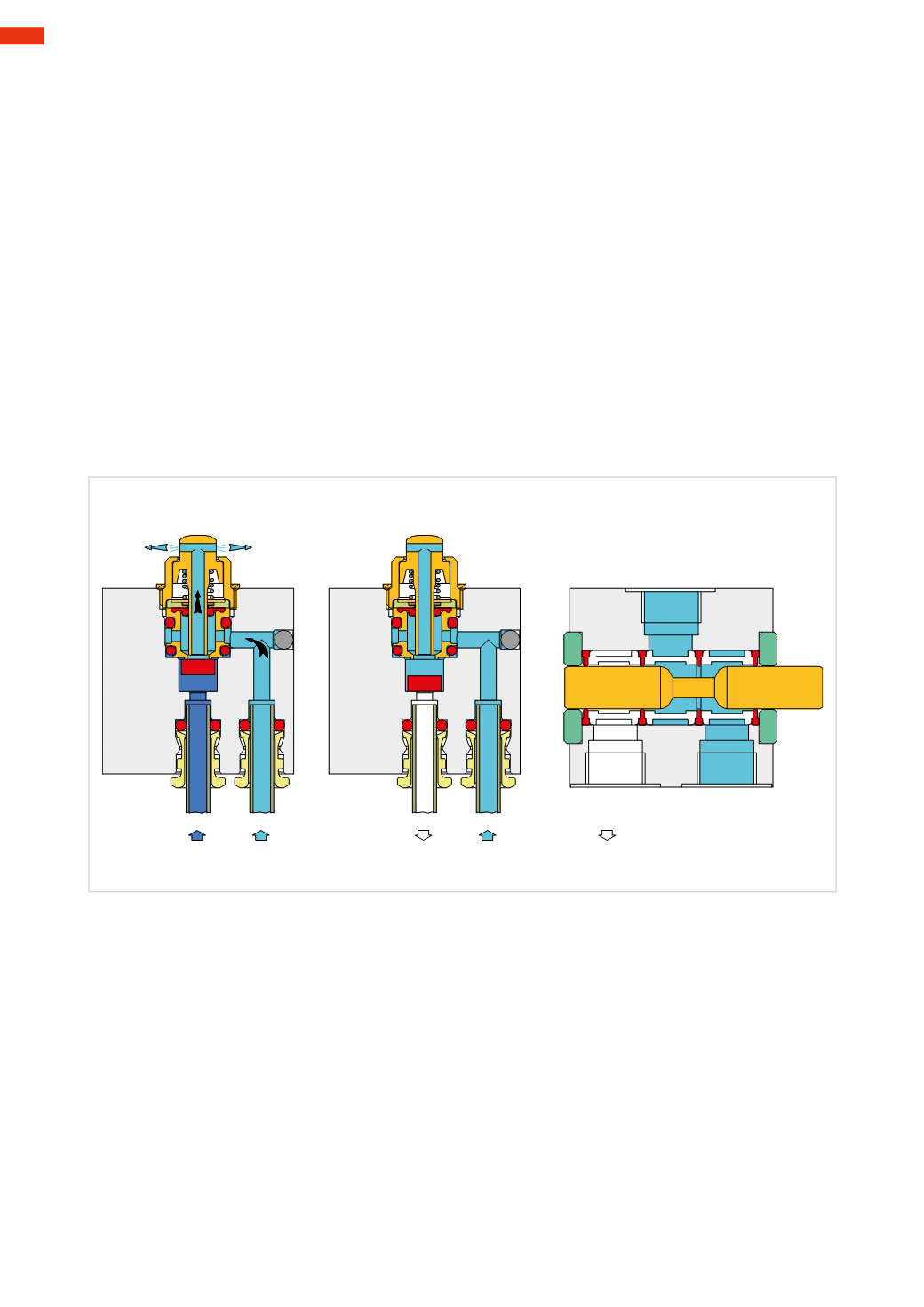
Figure 66
Pos. A
:
in a mini poppet valve, the presence of pressure at inlet 1 pushes the seal upwards towards the upper
orifice. In this case, we have anNC valve.
Pos. B
:
on the same valve the presence of a vacuum at inlet 1drags the seal downwards towards the lower orifice,
the valve does not respond to anymanoeuvre on the push button. Assuming there is a vacuum present at outlet 2,
we have the same situation as in Pos
A
, whereby the seal on the inlet is drawn upwards and there is continuous
passage through the exhaust 3, also in this case the valvewill not respond to anymanoeuvre on the push button.
Pos. C
:
a spool valvemay be used, whichwould depend on the geometry of the internal seals. Assumingwe apply
a vacuumat inlet 1, and the valve is in theNOposition, the vacuum is usableat connection2, exhaust 3 is closed.
Activating the spool closes the vacuum port 1 and connects atmospheric pressure to the outlet 2.
Assuming we apply a vacuum at exhaust 3, and the valve is in the NO position, the vacuum does not pass and
outlet 2 is at atmospheric pressure due to inlet 1.
By activating the spool the vacuum opens and closes communicationwith the atmospheric pressure.
There are generally no problems encounteredwith vacuum on spool valves withmechanical or manual operation;
on electrically operated valves, external piloting is necessary. In the case of directly operated solenoid valves,
generally no problems are encountered.
12
12
3
3
3
1
2
1
2
1
2
A
B
C
Fig. 66
4
130
CAMOZZI
>
VALVES

















