
CIRCUIT TECHNIQUE
Memory valves
The output signal generated by any monostable valve has the same duration as its pilot signal. These and other
signals can be processed through the logic functions
AND
and
OR
. The output signals from these two components
have the same duration as their input signals.
Inmany circuits, the short duration of one single signal may prevent the completion of the sequence, hence the
necessity for a valve that canmaintain the ONE state of a signal, i.e, to “memorize” the information.
Thememory valve is in fact a normal pneumatically operated bistable
3/2-way
or
5/2-way
valve.
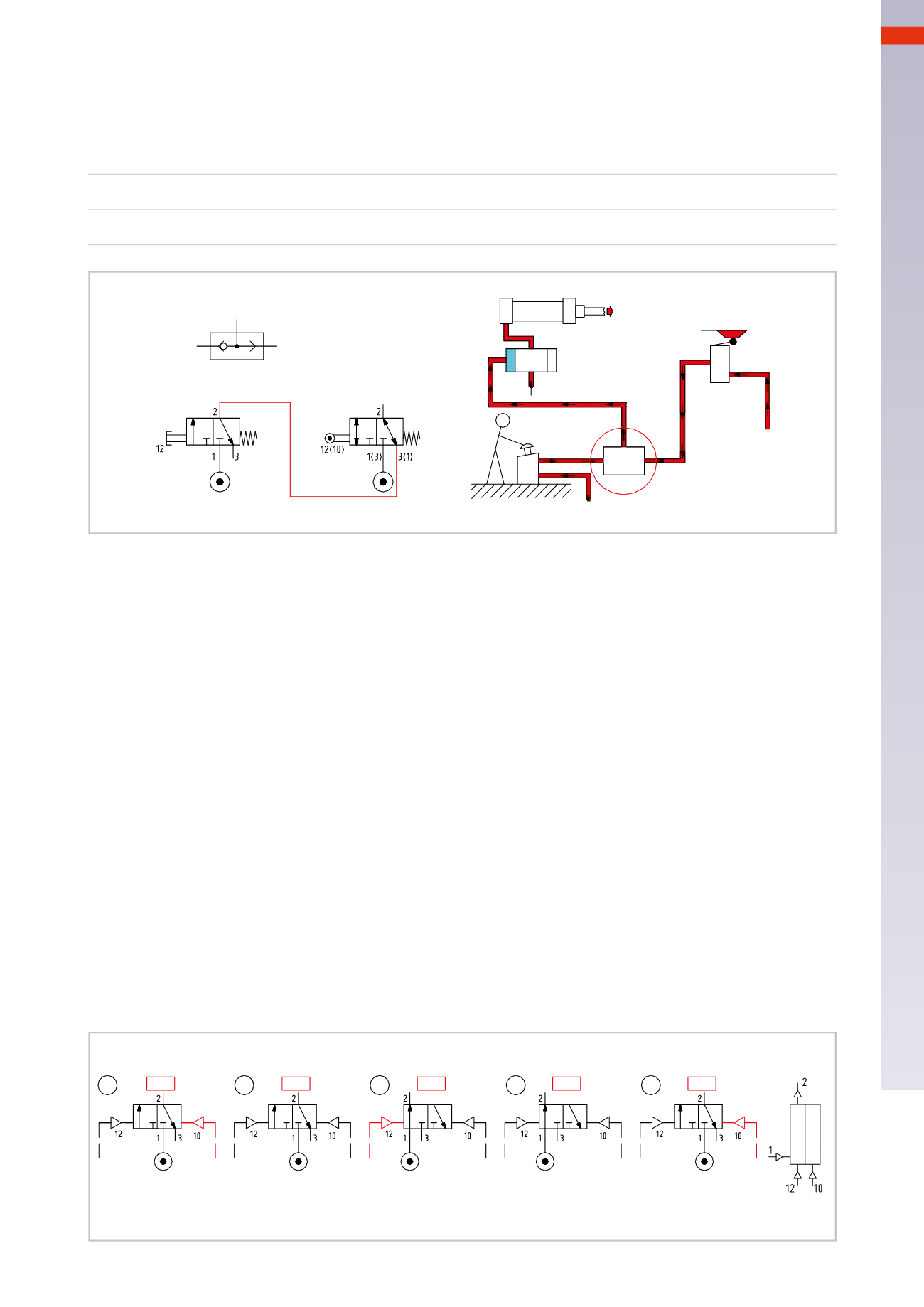
Figure 48
Operation of a 3/2-waymemory valve
Pos. 1
:
b
=
1 X
=
0
Pos. 2
:
b
=
0 X
=
0
the valve remains in the previous position
Pos. 3
:
a
=
1 X
=
1
signal “
a
” changes the valve over, putting inlet 1 in communicationwith outlet 2
Pos. 4
:
a
=
0 X
=
1
the valve remains in the previous position
Pos. 5
:
b
=
1 X
=
0
the valve has been positioned andmaintains its position even
in the absence of signal.
Thememory valve receives the signal
a
=
1
, which results in
X
=
1
.
This output will bemaintainedwith or without the presence of signal “
a
” as long as signal “
b
” is not given (signal
“
a
”must be removed).
1
2
3
4
5
X= 0
X=0
X= 1
X=1
X=0
b= 1
a=1
b=1
logic
symbol
(a) (b)
a= 0
b= 0
a=0
a= 0
a= 0
b= 0
b= 0
(X)
Fig. 48
a
b
a
b
a+b =X
a+b =X
Fig. 47
Figure 47
The valve that generates signal “
a
” will have its inlet 1 connected to the compressed air network, the valve that
generates signal “
b
” will have its inlet 1 connected to the compressed air network and its exhaust port connected
to the outlet of the first valve through port 3. This valve must be a spool valve. In this way the signal
X
can be
generatedwith the presence of only one signal from any of the two valves.
Logic equationwith the OR function:
a+ b= X
Logic equationwith 3/2-way valves:
a+ b= X
5
157
CAMOZZI
>
CIRCUIT TECHNIQUE

















