
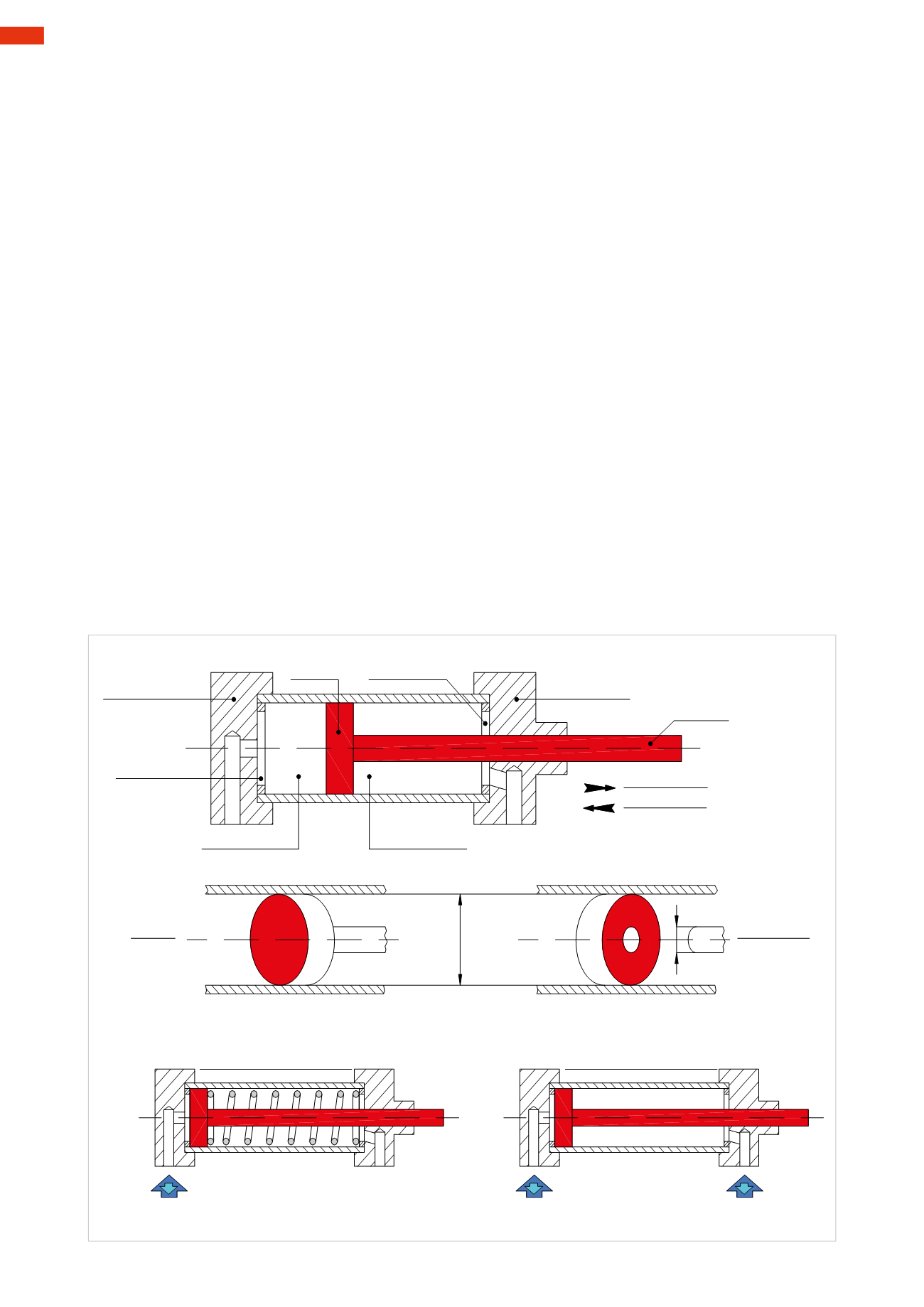
Rear end cap
Dead space
PositiveChamber
NegativeChamber
Piston
Dead space
Front end cap
PistonRod
PositiveStroke
NegativeStroke
D
D x
2
4
( D - d ) x
4
2
2
d
Single-acting cylinder (S/A)
Double-acting cylinder (D/A)
ц
ц
Fig. 5
Component parts and terminology
Figure 5
•
Tube/barrel
: is the part enclosed between the two end caps inside which the piston rod/piston entity runs;
the inside diameter, or bore, is the decisive factor in the choice of the cylinder.
•
Piston
:Moveswithin the barrel, separating the chamberswith seals; in some cases it integrates amagnetic ring
for detecting its position. Itsmovement is linear.
•
Piston Rod
: is the metal shaft connected to the piston and extends outside the cylinder to transmit the force
generated.
•
Frontandrearendcaps
:theyensurethemechanicandpneumaticsealingofthetubeandallowthe inletconnections
andairexhaust.Theycanhaveadjustingscrews fortheendstrokecushioningandmountingholes forthemounting
of the fixing elements (brackets) of the cylinder. The front-end cap integrates a guide bearing for the sliding of
the piston rod.
•
Dead space
: this is the remaining space between the end cap and piston at the end of the stroke.
•
Positive chamber
: this is the space between the piston and the rear end cap. Its volumewill vary depending on
the position of the piston.
•
Negative Chamber
: this is the space between the piston and the front-end cap. Its volumewill vary depending
on the position of the piston.
•
Active chamber
: chamber under pressure.
•
Passive chamber
: it is the exhaust chamber.
•
Positive stroke
: the direction of the piston rod/piston as it extends from the body.
•
Negative stroke
: the direction of the piston rod/piston as it re-enters the body.
•
Effective thrust area
: the surface area of the piston facing the positive chamber. This corresponds to the internal
section of the tube.
•
Effective pull area
: this is the surface onwhich the air exerts its pressure in the negative chamber. It is smaller
than the Effective Thrust Area because of the presence of the piston rod.
•
Single-acting cylinder (S/A)
: is realized in such a way that the return of the piston rod/piston occurs via an
internal spring. Usually air is applied to the positive chamber, driving the piston rod to its extended position.
The return stroke is achieved by a spring in the negative chamber. The negative chamber is always connected
to the atmosphere, and therefore never pressurized.
•
Double-acting cylinder:(D/A)
: is realized in such a way that the pressure can be exerted alternatively on both
sides of the piston. The piston applies a force in each direction.
3
56
CAMOZZI
>
CYLINDERS

















