
CYLINDERS
Example:
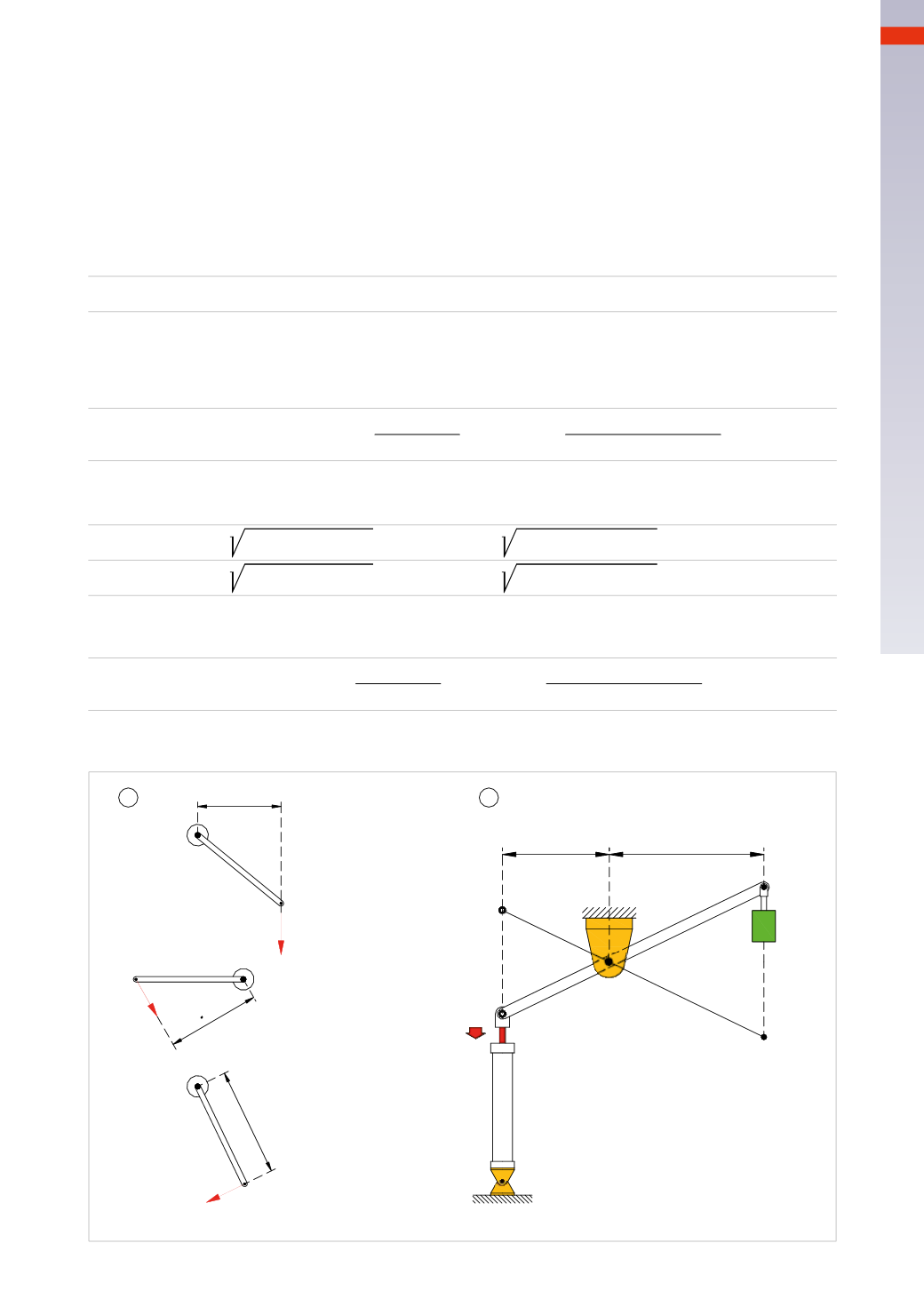
through a lever and a cylinderwe can lift a load and bring it into a position of equilibrium. It is possible to
achievebalancewith threedifferent positions of the cylinder relative to the fulcrumand resistance, as shownbelow.
Figure 19
Pos. 2
: the fulcrum
fc
is located between the power
P
and the resistance
R
(first type of lever).
Value of the load
R
= 12
Kg
(120
N
)
Lever length
PR
= 1100
mm
Distance of the fulcrum from the point of application of resistance
fcR
= 660
mm
Calculation of the distance of the fulcrum from the point of application of power
fcP
fcP
=
PR
–
fcR
=
1100 – 660=
440
mm
its state of equilibrium
RR
1
is possiblewith a displacement of 550
mm
.
Calculation of the cylinder stroke, using the similarity of the triangles
fcPP
1
and
fcRR
1
:
fcP
:
fcR
=
PP
1
:
RR
1
PP
1
=
fcP
1
*
RR
1
PP
1
=
440
[mm]
*
550
[m]
=
366
mm
fcR
660
[mm]
Using the
Pythagorean
theorem, we calculate the length of the arms
b
r
and
b
p
�
fcP
�
2
–
�
½
PP
1
�
2
b
p
=
�
440
�
2
–
�
½ * 366
�
2
≅
400
mm
b
p
=
�
fcR
�
2
–
�
½
RR
1
�
2
b
r
=
�
660
�
2
–
�
½ * 550
�
2
≅
600
mm
b
r
=
For the equilibrium of moments we know that:
b
p
* F
=
b
r
* R
F
=
b
r
*
R
F
=
600
[mm]
*
12
[N]
=
180
N
b
p
400
[mm]
The Force
F
required to bring balance into the system is 180
N.
arm
arm
arm
F
F
F
br
bp
R
P
1
P
fc
F
R
1
1
2
Fig. 19
3
69
CAMOZZI
>
CYLINDERS

















